Where does malaria occur
Malaria occurs in most tropical and sub-tropical areas of the world, including:
- Africa
- Central and South America
- Asia (including southeast Asia)
- Papua New Guinea
- Western Pacific islands
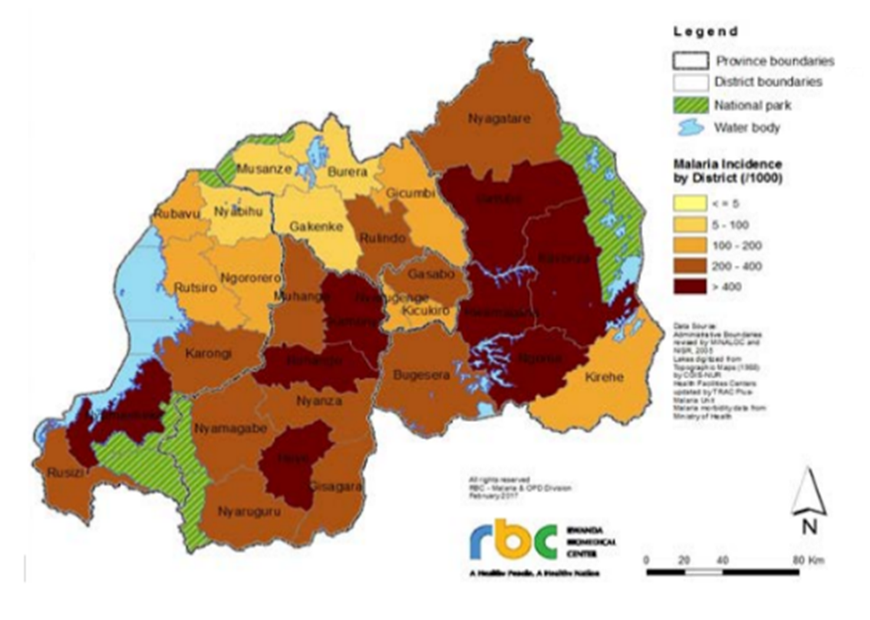
Malaria transmission risk areas in Rwanda
Rwanda is a land locked country in East Africa, bordered by Uganda, Burundi, Democratic republic of Congo and Tanzania. It has an area of 26,338 square kilometres with a population of more than 12 million people.
Malaria transmission in Rwanda occurs year-round with two peaks from May to June and from November to December following distinct rainy seasons. In Rwanda 19 of the 30 districts of the country are high endemic or malaria endemic zones with the Eastern and Southern provinces accounting for over 70% of the disease burden, and 11 endemic districts accounting for 56% of malaria cases in 2016. Of these, five districts are classified as high malaria burden districts including Bugesera, Gisagara, Gatsibo, Kirehe, and Nyagatare. See the map below.